Inference using Triton and TensorRT
Triton
This post will help you to run inference using Triton Inference Server. We will infer a model written in PyTorch. Following that, we will compile a model into TensorRT and infer that as well. For the code, a g4dn.2xlarge instance on EC2 (8 vCPU, 32 GB RAM, single T4 GPU) was used.
Make a directory structure like this
root@server:/work$ tree -L 1
├── models
├── pt
├── 1
├── trt
├── 1
First, we will pull the image for Triton
docker pull nvcr.io/nvidia/tritonserver:22.10-py3
We can start the server as
docker run --rm -it \
-v $(pwd):/work \
--name triton \
--gpus all \
-p 8000:8000 \
-p 8001:8001 \
-p 8002:8002 \
--runtime=nvidia nvcr.io/nvidia/tritonserver:22.10-py3 \
tritonserver \
--model-repository=/work/models \
--exit-on-error=false \
--repository-poll-secs=20 \
--model-control-mode="poll"
For inference, we need a few libraries.
pip install nvidia-pyindex
pip install tritonclient[all]
To check the status of the server, wait for 20s and execute the following. Proceed iff you get a 200 response code
curl -v localhost:8000/v2/health/ready
Copy your PyTorch scripted/traced model to the models/pt/1 directory.
Create a configuration file for this model
configuration = """
name: "pt"
platform: "pytorch_libtorch"
max_batch_size : 0
input [
{
name: "input__0"
data_type: TYPE_FP32
format: FORMAT_NCHW
dims: [ 3, 32, 32 ]
reshape { shape: [ 1, 3, 32, 32 ] }
}
]
output [
{
name: "output__0"
data_type: TYPE_FP32
dims: [ 10 ]
reshape { shape: [ 10 ] }
}
]
parameters: {
key: "INFERENCE_MODE"
value: {
string_value: "true"
}
}
"""
with open('/home/ubuntu/work/models/pt/config.pbtxt', 'w') as file:
file.write(configuration)
Wait for 20s and execute. Proceed iff you get a
curl -v localhost:8000/v2/models/pt
Make an inference request
import tritonclient.http as tritonhttpclient
VERBOSE = False
model_label = 'input__0'
input_shape = ( 3, 32, 32)
input_dtype = 'FP32'
output_name = 'output__0'
model_name = 'pt'
url = 'localhost:8000'
model_version = '1'
triton_client = tritonhttpclient.InferenceServerClient(url=url, verbose=VERBOSE)
model_metadata = triton_client.get_model_metadata(model_name=model_name, model_version=model_version)
model_config = triton_client.get_model_config(model_name=model_name, model_version=model_version)
Create a function to take an image as input and preprocess it.
import numpy as np
from torchvision import transforms
from PIL import Image
# preprocessing function
def img_preprocess(img_path="../GTC/img/cat.jpg"):
img = Image.open(img_path)
preprocess = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465], std=[0.2471, 0.2435, 0.2616]),
])
return preprocess(img).numpy()
transformed_img = img_preprocess()
Make the request
input0 = tritonhttpclient.InferInput(model_label, transformed_img.shape, datatype="FP32")
input0.set_data_from_numpy(transformed_img, binary_data=False)
output = tritonhttpclient.InferRequestedOutput(output_name, binary_data=False, class_count=10)
response = triton_client.infer(model_name, model_version=model_version, inputs=[input0], outputs=[output])
output_label = response.as_numpy(output_name)
You will see that it has returned the logits in a logit:class format. To convert it to a dictionary, we take the following steps
with open("../GTC/cifar10_classes.txt", "r") as f:
categories = [s.strip() for s in f.readlines()]
results = {}
for r in output_label:
cat = int(r.split(":")[1])
conf = float(r.split(":")[0])
results[categories[cat]] = conf
logits = list(results.values())
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
logits = torch.tensor(logits)
preds = (F.softmax(logits, dim=-1) * 100).numpy()
for c,k in enumerate(results):
results[k] = preds[c]
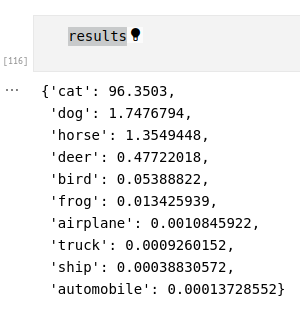
results
Here is a result obtained from inference
TensorRT
First, let’s pull the PyTorch container from Nvidia that includes TensorRT.
docker pull nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:22.10-py3
Convert the Torhscript model to TensorRT model via the following code
import torch
import torch_tensorrt
# load model
model = torch.jit.load("cifar10-script.pt")
# Compile with Torch TensorRT;
trt_model = torch_tensorrt.compile(model,
inputs= [torch_tensorrt.Input((1, 3, 32, 32))],
enabled_precisions= { torch.half} # Run with FP32
)
# Save the model
torch.jit.save(trt_model, "model1.pt")
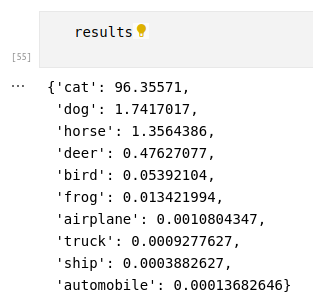
Note that we are using half precision, so our results might not exactly be the same.
Create the configuration file
configuration = """
name: "trt"
platform: "pytorch_libtorch"
max_batch_size : 0
input [
{
name: "input__0"
data_type: TYPE_FP32
format: FORMAT_NCHW
dims: [ 3, 32, 32 ]
reshape { shape: [ 1, 3, 32, 32 ] }
}
]
output [
{
name: "output__0"
data_type: TYPE_FP32
dims: [ 10 ]
reshape { shape: [ 10 ] }
}
]
"""
with open('/home/ubuntu/work/models/trt/config.pbtxt', 'w') as file:
file.write(configuration)
Wait for 30s and make sure you get a 200 Response code from the server
curl -v localhost:8000/v2/models/trt
Use the same preprocess function as above. Make the inference request (don’t forget to change the model name via model_name = 'trt'!)
You will get a similar result as above.
For the complete code, visit the repo.